Disadvantages of a passive crossovers
1 ) Back EMF (electromotive force) goes back into the crossover, interferes with the input signal from the amplifier.
2 ) Passive crossovers buffers the amplifier from the drivers resulting in loss of damping, loss of direct amplifier control over the drivers.
3 ) Loading effects, inductors, magnetic coupling, larger Cs, and parameters less adjustable.
4 ) Passive network wastes power, lowers efficiency, requires higher wattage amplifier to compensate.
5 ) Differing impedance of various drivers and the resulting phase shifts from the crossovers present a difficult load for the amplifier, especially 1st order crossovers.
6 ) Crossover properties and accuracy varies with power and temperature resulting in shifting properties and inconsistent linear response.
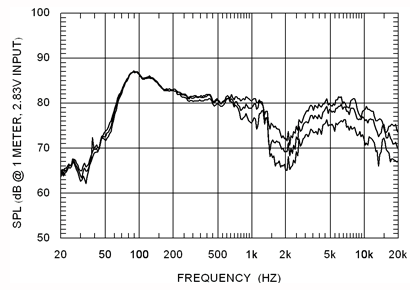
7 ) Low order crossovers reduces phase & time shifts but introduces other issues. Greater frequency sharing between drivers, and higher strain on drivers due to wider bandwidth demands increases distortion, both THD and intermodulation, induces interference patterns, amplitude irregularities, driver resonances, cone breakup, and hampers off-axis response.
8 ) High power draw in a specific frequency range, usually the bass, may cause amplifier clipping and possible damage to the woofer, midrange, or most likely, the tweeter. The amp has to deal with the combined complex impedance load and power draw.
Advantages of passive crossovers
1 ) Plug & Play simplicity.
2 ) One amp, one cable, done.
Disadvantages of active crossovers
1 ) Residual noise from crossover, less of an issue for digital processors.
2 ) Greater susceptibility to EMI (electromagnetic interference), and RFI (radio frequency interference).
3 ) Multiple amps & cables, more complex setup.
Advantages of active crossovers
1 ) Direct control of each driver by its own amplifier.
2 ) Easier impedance load on the amp.
3 ) No loss of power or damping factor.
4 ) Reduced clipping. If clippings occurs, only one driver/amp is affected.
5 ) Crossover works at line level maintaining its design properties.
6 ) Each amp deals with only a specific bandwidth.
7 ) Reduced harmonic distortion.
8 ) Reduced intermodulation distortion.